- The Missing Link: Learn why focusing solely on calcium and Vitamin D is insufficient for bone health and can even be dangerous without adequate Magnesium.
- The Locksmith: Magnesium is the essential cofactor that allows calcium to be moved out of the bloodstream and into the bone structure, preventing arterial calcification.
- The Simple Fix: Most people are deficient. Discover a 60-second snack swap that can easily meet your daily magnesium needs and instantly boost bone density.
The Calcium Illusion
For decades, we have been told a simple story about bone health: Calcium is the key, and milk is the answer.
“Got Milk?” campaigns drilled into us the singular idea that if we want strong bones and protection against osteoporosis, we must flood our bodies with calcium. While calcium is undeniably vital—it provides the structural scaffolding for our skeletons—this focus has become a massive, and dangerous, oversimplification.
I have witnessed countless clients who religiously consume their calcium supplements and dairy products, yet their bone density scans continue to show trouble. Worse, some develop unexplained kidney stones or even signs of arterial hardening (calcification).
Why?
Because a building is not constructed with only bricks. You need mortar, scaffolding, and, most importantly, a construction manager to tell the bricks where to go.
In the human body, calcium is the brick. The construction manager is a mineral that 50–80% of adults are silently deficient in: Magnesium.
Magnesium is the great unsung hero of the human body, involved in over 300 biochemical reactions. But its role in bone health is non-negotiable. Without sufficient magnesium, the calcium you meticulously consume cannot perform its job correctly. It can’t enter the bone structure, and worse, it can get deposited in places you absolutely do not want it—like your arteries.
Let’s unpack the science of this critical partnership and learn how to flip the switch for maximum bone density.
The Silent Epidemic: Why Magnesium Deficiency is Missed
Before we discuss how magnesium works, we must address why so many people are deficient, even while eating what they believe is a balanced diet.
1. Soil Depletion
The magnesium content in our food has plummeted over the last century due to modern farming techniques that prioritize yield over nutrient density. Magnesium is the central atom of the chlorophyll molecule—the green pigment in plants. As soil quality declines, so does the magnesium content of our fruits, vegetables, and grains.
2. The Stress Drain
Magnesium is the body’s natural muscle relaxant and stress buffer. When we are under chronic stress (physical or emotional), our body rapidly uses up magnesium to manage the fight-or-flight response. The modern lifestyle is essentially a massive, chronic magnesium drain.
3. Faulty Testing
The biggest reason this deficiency is silent is that standard blood tests are unreliable for assessing magnesium status. Approximately 99% of the body’s magnesium is stored inside cells and bone. Only about 1% circulates in the blood. If your body senses blood levels dropping even slightly, it will furiously pull magnesium out of your bones to keep the blood stable—meaning your blood test looks fine while your bones are simultaneously being robbed.
The Warning Sign: If you suffer from frequent muscle cramps, twitches, persistent anxiety, or poor sleep, these are often the earliest, clearest signs that your magnesium stores are critically low, and your bone-building efforts are paralyzed.
The Magnesium-Calcium Locksmith Mechanism
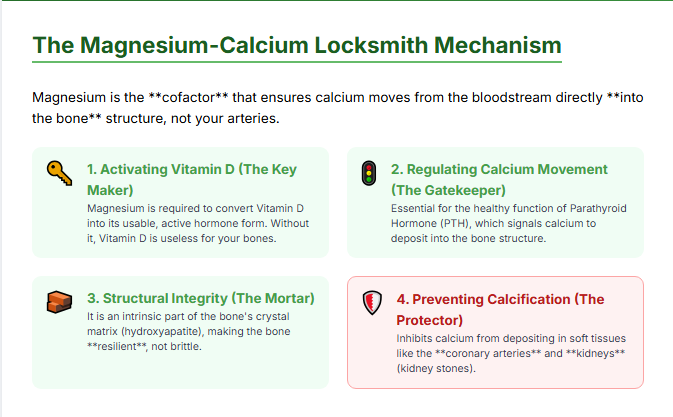
Magnesium doesn’t just “help” calcium; it is the Locksmith that allows calcium to enter the bone and prevents it from turning into a threat. This partnership works on four critical levels:
1. Activating Vitamin D (The Key Maker)
We often hear that Vitamin D is necessary for calcium absorption. This is true. However, Vitamin D is biologically inactive until it is processed by the liver and kidneys. This conversion process—turning Vitamin D into its usable, active hormone form—requires magnesium as a cofactor.
If you take large doses of Vitamin D but are magnesium deficient, you are creating a huge amount of unusable, circulating Vitamin D, which is useless for your bones and can actually increase toxicity risks. Magnesium is the master switch for Vitamin D function.
2. Regulating Calcium Movement (The Gatekeeper)
When calcium levels in the blood need to be regulated, the body relies on the Parathyroid Hormone (PTH). PTH controls whether calcium is kept in the blood or moved into the bone. Magnesium is absolutely essential for the healthy release and function of PTH. Without it, the body can’t properly signal calcium to deposit into the bones.
3. Structural Integrity (The Mortar)
When calcium and phosphorus form the crystal structure of the bone (hydroxyapatite), magnesium is intrinsically part of that crystal matrix. It helps determine the density and strength of the final bone structure, ensuring that the bone remains resilient, not brittle.
4. Preventing Soft Tissue Calcification (The Protector)
This is the most crucial, life-saving role. When you consume too much calcium without enough magnesium, that excess calcium tends to float in the bloodstream. Magnesium helps regulate the proteins (like matrix Gla protein) that inhibit calcification in soft tissues. Without enough magnesium, calcium may deposit where it doesn’t belong:
- In the kidneys, leading to painful kidney stones.
- In the coronary arteries, leading to arterial hardening (atherosclerosis), a major risk factor for heart attack and stroke.
The message is clear: Magnesium ensures calcium goes into your bones, not your arteries.
The Simple Fix: Boosting Magnesium Naturally
Since the magnesium deficiency is primarily driven by diet and lifestyle stress, the fix involves making small, targeted changes to your food choices.
You don’t need a complex new supplement routine to start fixing this. You need to swap one daily habit.
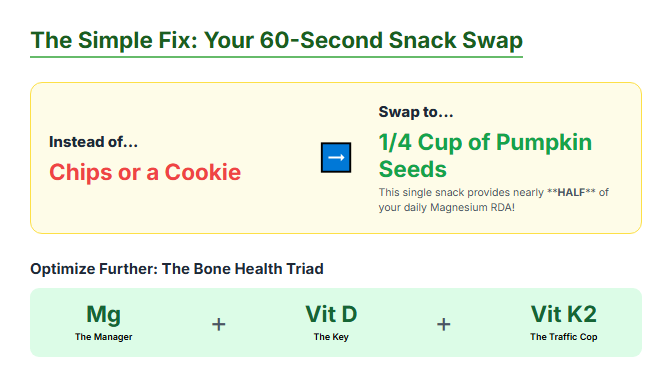
1. The 60-Second Snack Swap (Your Daily Magnesium Dose)
This is the easiest, most effective way to start getting your magnesium:
- Instead of: A bag of chips or a cookie.
- Swap to: 1/4 cup of Pumpkin Seeds (Pepitas). A 1/4 cup serving of pumpkin seeds contains nearly half of your Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for magnesium. They are delicious, easy to snack on, and fit seamlessly into your day.
- Other Top Swaps: Almonds, chia seeds, dark chocolate (80% cocoa or higher), and cashews are all magnesium powerhouses.
2. Prioritize “The Greens”
Because magnesium is the center of the chlorophyll molecule, the darker the green, the more magnesium you get.
- The Green Power Rule: Incorporate a large serving of Spinach or Swiss Chard into your dinner every day. Use them in smoothies, toss them in eggs, or sauté them lightly.
3. Address the Water Factor
If you live in an area with soft water, your drinking water likely lacks beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium. People in soft water areas tend to have higher rates of cardiovascular issues. If you rely on reverse osmosis (RO) water purification, remember that this process strips all minerals—you must add them back.
Beyond Bones: The Systemic Benefits of Magnesium
When you optimize your magnesium levels, you are not just strengthening your skeleton; you are upgrading your entire nervous system. The benefits of correcting this deficiency are systemic and immediately noticeable:
- Deeper, Restorative Sleep: Magnesium helps activate the GABA receptors in the brain, which are responsible for calming the nervous system, leading to quicker sleep onset and deeper rest.
- Anxiety and Mood Regulation: Magnesium helps modulate the stress response, physically relaxing tension in the body and brain.
- Fewer Muscle Cramps: Magnesium’s role as a natural muscle relaxant can eliminate chronic leg and foot cramps, especially those that strike at night.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium plays a key role in insulin sensitivity, making your cells more receptive to insulin and helping to manage blood sugar spikes.
My Personal Strategy: The Daily Magnesium Ritual
I treat magnesium optimization as a non-negotiable component of my health. My primary rule is: Food first, then targeted supplementation.
- Morning Fuel: I ensure my breakfast always contains some form of magnesium (chia seeds in oatmeal, or almonds in yogurt).
- Nightly Dose: For systemic relaxation and deep sleep, I use a targeted form of magnesium at night. I am personally a huge advocate for topical application—a quick foot or leg rub with magnesium oil or lotion is incredibly effective because it bypasses the digestive tract, preventing the laxative effect many people associate with oral supplements.
This two-pronged approach ensures I maximize my intake from food while using supplementation to actively manage the stress drain.
Myths vs. Facts About Magnesium
Myth: “If I take a calcium supplement, I’m fine.”
Fact: If your calcium-to-magnesium ratio is unbalanced (too much calcium, too little magnesium), you are increasing your risk of calcification in soft tissues. Calcium supplements often need to be counterbalanced with magnesium supplementation.
Myth: “I can’t take magnesium; it gives me diarrhea.”
Fact: The form of magnesium you use matters! Magnesium oxide and citrate are often used as laxatives because they are poorly absorbed. Forms like Magnesium Glycinate (for sleep/anxiety) and Magnesium Malate (for muscle recovery) are much more easily absorbed and rarely cause digestive issues.
Myth: “I only need magnesium if I have bone problems.”
Fact: Magnesium is critical for energy production (it’s required to make ATP), DNA repair, and nerve signaling. If you are breathing, eating, or stressing, you need magnesium.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the best form of magnesium supplement?
There is no single “best” form, as they target different tissues:
- Magnesium Glycinate: Best for sleep, anxiety, and general deficiency. Highly bioavailable and gentle on the stomach.
- Magnesium Malate: Best for muscle pain and recovery.
- Magnesium L-Threonate: The only form known to readily cross the blood-brain barrier; best for cognitive function and memory.
2. Can I get too much magnesium?
Toxicity from food alone is nearly impossible, as your kidneys are highly efficient at excreting excess magnesium. However, very high doses of supplements (over 5,000 mg) can lead to diarrhea or stomach upset. Stick to the RDA (around 320 mg for women, 420 mg for men) and only supplement under guidance if aiming for higher therapeutic levels.
3. Should I take Vitamin K2 with magnesium?
Absolutely. Vitamin K2 is another vital “traffic cop” that works with magnesium. K2 specifically activates the proteins (like osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein) that ensure calcium is deposited into the bone structure and removed from the arteries. Magnesium, K2, and Vitamin D are the essential Bone Health Triad.
Conclusion
We were taught a simple but incomplete story about calcium. Now, we know the full, complex truth.
Building strong, resilient bones isn’t just about loading up on one mineral; it’s about supplying the entire team of cofactors necessary to manage your body’s systems—and that team is led by magnesium.
If you want to protect your bone health, stabilize your mood, and ensure calcium is healing your skeleton instead of hardening your arteries, start today. Change that one snack, and empower the “master mineral” to perform its vital work.
Medical Disclaimer: I am a health advocate and writer, not a medical doctor. The information in this article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.



